Introduction to auditing
Unit 1
INTRODUCTION TO AUDITING
Introduction – Meaning - Definition – Objectives – Differences between Accountancy and Auditing – Types of Audit - Advantages of Auditing – Preparation before commencement of new Audit – Audit Notebook – Audit Working Papers – Audit Program, Recent Trends in Auditing: Nature & Significance of Tax Audit – Cost Audit - Management Audit. Forensic audit Tally ERP 9 Auditors Edition: Introduction, features, characteristics – Tally.Net: features – requirements for remote connectivity – Access information via SMS, Safeguard Data – Automated Backup and Recovery. E-Auditing-meaning, uses and limitations, auditing the auditor
Meaning of auditing
Audit is the examination of various books of accounts by an auditor followed by physical checking of inventory to make sure that all departments are following documented system of recording transactions.
Definition of auditing
some of the definition are: “Auditing is an examination of accounting records undertaken with a view to establishment whether they correctly and completely reflect the transactions to which they purport to relate.”-L.R.Dicksee
“Auditing is concerned with the verification of accounting data determining the accuracy and reliability of accounting statements and reports.” - R.K. Mautz
“Auditing is the systematic examination of financial statements, records and related operations to determine adherence to generally accepted accounting principles, management policies and stated requirement.” -R.E.Schlosser
Indian Accounting Standards-Unit 1 click here
Finance Group-Strategic Finance Management (SFM) Unit1
Objectives of Auditing
The objectives of the auditing have been classified under two heads:
1) Main objective
2) Subsidiary objectives
1) Main Objective:
- To find reliability of financial position and profit and loss statements.
- To verify and establish that at a given date balance sheet presents true and fair view of financial position of the business and the profit and loss account gives the true and fair view of profit or loss for the accounting period.
- To establish that accounting statements satisfy certain degree of reliability.
- To form an independent judgement about the reliability of accounts and truth
2)Subsidiary objectives:
The subsidiary objectives of the auditing are:
i. Detection and prevention of errors:
Error of Principle-Where the recording of the items of transactions are not done according to the Principle of Accounting, it is known to be an error of principle.
Error of omission-is the omission of entry while recording the transactions in the books of accounts;
Error of duplication-The detection of error of duplication is very difficult. It might be detected with proper and minute observation of accounts; for example, purchase may be recorded twice with original and duplicate copy of purchase invoice, etc.
Error of commission occurs the entry made in the books of the original entry or the ledger account is wrong.
Compensating errors-When the effect of an error compensates with another error; it is known to be a compensating error.
ii. Detection and prevention of fraud:
The following are the distinct types of fraud −
- Misappropriation of Cash-Theft of cash receipts and petty cash and showing fictitious payment to workers, creditors, purchases, etc.Showing false payments or excess payments in cash book
- Misappropriation of Goods-can be done in the following ways −Goods may be stolen by employees or with the help of employees by issuing false credit notes to customer on account of goods return.
- Manipulation of Accounts-Two types of manipulation of accounts are done by top management to mislead some parties for some specific purpose like showing higher profits and showing lower profits
- Misappropriation of assets.
- Suppression of effect of transactions from records
- Recording of transactions without substance.
- Misapplication of accounting policies
Advantages of auditing
- It helps to detect errors and frauds and thus helps to minimize the risks of errors and frauds in the books of accounts
- It gives assurance to the owners/investors about the accuracy of their books of accounts.
- Audited accounts are considered more reliable for taxation purpose
- Audited accounts are easily accepted by insurance companies for settlement of claims.
- Audited financial statements are acceptable by bank and financial institutions and helpful in getting loans and credit facilities.
- Creditors of an organization also rely on audited financial statements and accordingly grant credit limit to business entities.
- Taxation authorities and all other Government authorities rely on audited financial statements; even the courts accept these as evidence when the situations call for.
- It ensures compliance that policies and procedures are in place to protect the public interest and their practices are compliant with best practices and effective for the organisation.
- It helps with business improvements as auditing is a way to test the system and identify opportunities that can be used to improve business performance.
- Provides credibility – It offers credibility because it allows you to run your business without fear of being discovered for some kind of fraud.
- Useful for Planning and Budgeting – It plays a significant role in finding hidden risks or opportunities within the planned activities.
Auditor
An auditor is a person who conducts audit.He is authorized to review and verify the accuracy of financial records and ensure that companies comply with tax laws. They protect businesses from fraud, point out discrepancies in accounting methods
Qualities of an auditor
An auditor should be a qualified Chartered Accountant or he should be a qualified member of The Institute of Cost & Works Accountants of India to do cost audit.Apart from the professional qualification,an auditor must possess the following qualities
1.The auditor must have a complete and thorough knowledge of the principles, theory and practice of accountancy.
2. He should have a thorough knowledge in various legislation regulating business such as Companies Act,Banking and Insurance Act,Sale of Goods Act, Foreign Exchange Management Act, the Indian Contract Act, etc.
3. The auditor should have a thorough knowledge of the techniques of auditing. He should be fully aware of new changes and developments in the principles and practice of auditing.
4. The auditor must be familiar with the computer accounting and other automatic machine devices used in the office.
5. In addition to the knowledge of commercial laws, an auditor should have knowledge of the various provisions relating to income tax wealth tax, VAT, gift tax, etc.
6. An auditor must be vigilant and honest in his work
7)An auditor must have the ability to write audit report correctly , precisely, concisely, and clearly
8)The auditor should have the ability to maintain secrets and should not disclose the secrets of his client to anybody
Accounting means systematically keeping the records of the accounts of an organization and preparation of financial statements at the end of the financial year whereas Auditing means inspection of the books of account and financial statements of an organization.
Accounting is governed by accounting standards whereas auditing is governed by standards on auditing
Accounting is a continuous process, i.e. day to day recording of transactions are done.Auditing is a periodic process.
Accounting starts where bookkeeping ends.Auditing starts where accounting ends.
The purpose of accounting is to show the performance, profitability and financial position of an organization whereas the purpose of auditing is to reveal the fact, that to which extent financial statement of an organization gives true and fair view
Types of audit
Types of audit
I.Based on ownership
I.On the basis of ownership audit can be:-
1. Audit of Proprietorship: In this case , the owner himself takes the decision to get the accounts audited. Sole trader will decide about the scope of audit and appointment of auditor.
2. Audit of Partnership: Here partners audits their accounts. Partnership deed on mutual agreement between the partners may provide for audit of financial statements. Auditor is appointed by the mutual consent of all the partners.
3. Audit of Companies: Under companies Act, audit of accounts of companies in India is compulsory. Chartered accountant who is professionally qualified is required for the audit of accounts of companies.
4. Audit of Trusts: The trustees are appointed to manage and look after the property and business of the trust. Accounts of the trust are maintained as per the conditions and terms of the trust deed.
5. Audit of Accounts of Co-operative Societies: The auditor of the Co-operative Society should have an expert knowledge of the particular act under which Co-operative society under audit is functioning. The Registrar of co-operative societies shall audit the accounts of the society once in every financial year.
6. Government Audit: Audit of government offices and departments is covered under this heading. A separate department is maintained by government of India known as Accounts and Audit Department. This department works only for the government offices and departments.
II. Based on Time:
On the basis of time the audit can be of following types:
1. Interim Audit: When an audit is conducted between two annual audits, such audit is known as Interim audit. It may involve complete checking of accounts for a part of the year.
2. Continuous Audit: The Continuous Audit is conducted throughout the year or at the regular short intervals of time. A continuous audit is one where the auditor or his staff is constantly engaged in checking the accounts during the whole period
3. Final Audit: Final Audit means when the audit work is conducted after the close of financial year. It is not commenced until after end of the financial period and is then carried on until completed.
4. Balance Sheet Audit: Balance Sheet Audit relates to the verification of various items of balance sheet such as assets, liabilities, reserves and surplus, provisions and profit and loss balance.
III.Based on Objectives:
On the basis of objectives the audit can be of following types:
1. Internal Audit: It implies the audit of accounts by the staff of the business. Internal audit is an appraisal activity within an organization for the review of the accounting, financial and other operations as basis for protective and constructive service to the management.
2. Cost Audit: Cost Audit is the verification of the correctness of cost accounts and adherence to the cost accounting plans.
3. Secretarial Audit: Secretarial Audit is concerned with verification compliance by the company of various provisions o Companies Act and other relevant laws.
4. Independent Audit: Is conducted by the independent qualified auditor. The purpose of independent audit is to see whether financial statements give true and fair view of financial position and profits.
5. Tax Audit: Tax audit mostly covers income returns, invoices, debit and credit notes and various current and fixed assets. . Tax audit ensures the validity and credibility of tax related documents
Preparation before commencement of new Audit
Verification of Appointment: First of all auditor has to conform whether his appointment is properly made or not. If appointment is not proper, he can claim remuneration, if he is appointed by share holders, he has to see whether the procedure specified under Section 224, is properly followed or not. If he is appointed by directors he has to go through the resolution made by the court.
Verification of Memorandum: Memorandum deals with external affairs of the company. The information written under objects clause, liability clause and capital clause is useful to auditor. Therefore he should refer to memorandum and such information should be taken to audit notebook.
Verification of Articles: Articles includes calls on share, transfer of shares, transmission of shares, reserves, payment of dividend etc. All these are useful to Company auditor and hence abstracts from articles should be taken to audit notebook.
Verification of Prospectus: Before commencing the audit work, auditor should refer to prospectus to obtain information relating to minimum subscription, preliminary expenses, underwriters commission etc.
Verification of Contract Deeds: On account of legal entity company can enter into contracts. Auditor should refer to those contract deeds to know about names of parties to the Contract, Contract prices, other terms etc.
Verification of Certificate of incorporation and certificate of Commencement of business: If it is first audit of the company, auditor should refer to Certificate of Incorporation and Certificate of Commencement of Business issued by registrar of Companies to conform that the company has got formed properly in accordance with requirements of companies act.
Verification of Internal Check System: Internal check means arrangement of staff in such a way where work done by one clerk automatically gets checked by the other. Well planned internal check system minimizes scope for frauds and errors.
List of Books: Auditor should obtain list of books maintained by the company. Company maintains several statutory books , Statistical books, Cost records, financial records etc. All those books are to be listed.
List of Offices: Auditor should refer to organization chart of the company and has to gather names, rights, duties, specimen signatures etc of staff members employed in such key positions.
Audit Notebook – Audit Working Papers
Audit working papers are used to document the information gathered during an audit. They provide evidence that sufficient information was obtained by an auditor to support his or her opinion regarding the underlying financial statements.
Working papers also provide evidence that an audit was properly planned and supervised. Audit working papers are prepared by the audit staff and audit seniors, and are reviewed by audit senior managers and partners
The forms of documentation that may be contained within the working papers include the following:
Checklists of standard investigation items that were completed, and by whom
Copies of correspondence
Documentation of the assertions investigated and supporting evidence found
Extracts from the corporate minutes of the client
Flowcharts of a client's key transaction processes
Narrative discussions of issues found
Organization charts
Questionnaires for which the client provided answers
Audit Program
Audit programme represents an outline of procedure to be followed to support an opinion on financial statements. It is the auditor’s plan of action. It provides a plan of work of examination and a set of audit procedures.
It contains details regarding the relevancy of evidence, materiality level, risk tolerance, measure of the sufficiency of the evidence. Thus, programs enhance the accountability of the audit team and its members for the work performed by them.
Recent Trends in Auditing:
Artificial Intelligence (AI)-AI has been a swiftly accelerating trend across most areas of business in recent years, and as such, brings risks and challenges to overcome alongside the benefits. Internal audit has already proven its worth in helping to integrate governance, controls, and risk management across automation initiatives during digitisation, transformation or change management processes.
Soft controls and company culture-Company culture is becoming an increasingly important subject to many organisations and has been pinpointed as an important part of any company’s talent attraction and retention strategy. When top talent is in scarce supply, company culture and employee satisfaction should be a top priority for all.
A holistic approach to third-party risk management-Internal audit has had a greater focus on assessing third-party vendors’ means to support themselves with a robust framework in place should there be future disruption to supply chains. Beyond contract management, internal audit will examine the proficiency of remodelled supply chains and assess the risk they pose.
Nature and significance of Tax audit
- Tax Audit refers to the verification of the books of accounts of the taxpayer. The auditor examines or reviews the books to form an opinion on matters related to taxation compliances that are carried out by the assessee.
- The assessee must comply with the provisions of the Income Tax Act, 1961, while preparing the books of accounts, particularly from Section 28 to Section 44DB.
- According to Chartered Institute of Management Accountants, London (C1MA), cost audit is “the verification of the correctness of cost accounts and of the adherence to the cost accounting plan”. In other words, cost audit is the verification of the cost of production of any product, service or activity on the basis of accounts maintained by an enterprise in accordance with the accepted principles of cost accounting. This definition of Cost Audit is relevant to the voluntary Cost Audit without any statutory backing.
The objectives of the tax audit are as follows:
- An analysis of the accuracy of income tax returns filed in the assessment year by companies and individuals and maintenance of records by the Chartered Accountant (CA).
- Report the findings by the tax auditor after making precise analysis of accuracies or inaccuracies in the filed tax returns.
- Tax audit checks on all the frauds and malpractices in filing income tax returns.
- To report the essential details with regard to compliance, tax depreciation, etc., as per the income tax laws. These streamline the processes for the authorities of income tax in the calculation and also assessing the accuracy of the income tax return filed by the individual or company.
- A management audit is an assessment of how well an organization's management team is applying its strategies and resources.
- A management audit evaluates whether the management team is working in the interests of shareholders, employees, and the company's reputation.
- A forensic audit examines and evaluates a firm's or individual's financial records to derive evidence used in a court of law or legal proceeding.1Forensic Audit
Forensic audits cover a wide range of investigative activities. A forensic audit is often conducted to prosecute a party for fraud, embezzlement, or other financial crimes. In the process of a forensic audit, the auditor may be called to serve as an expert witness during trial proceedings.
Forensic auditing is a specialization within accounting, and most large accounting firms have a forensic auditing department. Forensic audits require accounting and auditing procedures and expert knowledge about the legal framework of such an audit.
Tally is one of the most popular and powerful Indian accounting software used extensively in India. It is driven by a technology called concurrent, multi-lingual, accelerated technology engine.
Tally.ERP9 is much more than just accounting. The term “ERP” stands for Enterprise Resource Planning in very technical terms. The data in Tally is fully integrated which saves a lot of time and efforts.Tally.ERP 9 has an inbuilt feature- Tally Audit which enables the auditor to perform an audit or track changes that affect the integrity of a transaction, such as changes made to Date, Ledger Masters and Amounts in the Voucher are reflected in the Tally Audit Listings.
Tally.ERP 9 Auditors Edition
Tally.ERP 9 Auditors Edition (AE) is designed in such a manner that it fulfils the requirements of the clients. Tally is extremely simple and easy-to-use accounting software. It offers efficient and effective solutions and services to the organisations to manage their routine operations, and generates required business reports, which helps them take strategic decisions vital for the growth of their business. This is one of the most popular accounting software for various business organisations.
Some of the attributes of the software are simple accounting management, easy to share files, flexible inventory management, taxation, outstanding management, budget and control, one-stop solution for compliance, faster access to business reports, payroll management, profit centre management, multilingual capabilities, and easy application management.
It has all the features required for high performance of business management including remote access, audit and compliance service, integrated support centre, security management etc. The software is designed in such a manner that, it can be customized according to your business requirement. For every business which require solutions for maintaining invoices to accounting and inventory management, Tally.ERP is the right choice.
B] Key Features of Tally.ERP 9 Auditors Edition
- Helps in comparing the financials of current as well as previous years, thereby identifying the discrepancies and resolving them.
- Generates Tax Audit reports & annexures to support in auditing.
- Permits the Column sorting & multi-selection of vouchers during auditing.
- Identifies and reports errors in data.
- Reviews & verifies tax-liability through an all-in-one dashboard.
- Filter transactions for further processing.
- Keeps a track on the work quality and assist clients to file their tax returns on time.
C] Benefits of Tally.ERP 9 – Auditors’ Edition
- Increase Audit Efficiency:-
- Reduce Time and Effort:-
- Additional Scope of Work:-
- File Unlimited GST Returns from Tally ERP 9:-
- Cost Centres or Profit Centres Management in Tally ERP 9:-
Tally.ERP 9 – Auditors’ edition helps auditors accessing client’s records remotely. They don’t need to be physically present at the client’s location to perform the audit. Gone are the days when an audit was performed manually, and there were lots of redundancy and duplication. With this enhanced version of Tally, doubts can be raised and clarified within the software.
The auditor version has special capabilities to assist in regular Statutory Compliance without needing to visit the client site. Thus, the reasons for non-compliance can be quickly identified.
Since considerable time is saved in the routine tasks, a practising Chartered Accountant can offer additional Business Advisory services to the clients. They can play the role of virtual CFOs and help businesses track the numbers in real-time. The tool helps to enhance revenues, reduce unnecessary time and delays, and offers better services.
CA’s can file unlimited GST returns from the auditor’s version of the Tally for all the clients.
With the help of cost centre feature one can easily track the cost of the business centre/location wise. For instance, if you are selling shoes, you can create different cost centres for different manufacturing locations. You can also create different profit centres for branches through which you sell the shoes.
D] Reporting in Tally
To take vital decisions, management needs well-structured reports. Reports provide a specific idea of the present performance of the business or a project. Tally software offers a variety of reports using which management can critically analyze the performance of the business and decide the future course of actions.
Tally also has the feature of providing various reports such as GSTR-1, GSTR-2, GSTR-3B related reports. The format of GSTR-1 is like the GSTR-1 form. This makes it easier for the user while filing the GST return.
Tally.NET Services
On a broad level, Tally.ERP 9 comprises of:
• The product itself
• A set of capabilities (enabled via the Internet) by a service called Tally.NET
This 'two component' architecture was chosen as this delivers an unparalleled model of a host of services as below:
(Tally.NET Services Annual Subscription is included in your Tally.ERP 9 for the first one year. Subsequently you are advised to subscribe to avail the following services at a nominal charge of 20% of the then prevailing product price)
(a)Remote Access Services
Your business data stays with you locally, and is never stored on Tally.NET servers or on systems accessing that data via Remote Access.
(b)Integrated Support Services - Support Centre
Integrated within Tally.ERP 9 and Shoper 9, this new feature enables the users to report and track their queries from within the product. You can directly target the query to your regular Tally Service Provider (or any other Tally Service Provider, if you are making your first query) and get responses quickly. These can even be reported and viewed remotely. You can then use the reference number to escalate the issue to Tally’s Customer Centre in case you need to.
Over time, this capability will be extended to cover your Chartered Accountant or other business associates & friends using Tally.ERP 9 to broaden the horizon of your support ecosystem.
You can also access all the conversations centrally. This will simplify the process of having a summary view of the kinds of issues people in your company raise – which will help you identify gaps of knowledge or other persistent system issues.
(c)Self-service using Control Centre
The Control Centre enables users to centrally configure and administer Site/ User belonging to an account. Thus the Control Centre acts like an interface between the user and Tally.ERP 9 installed at different sites.
With the Control Centre you save time, travel and communication costs, manage Tally.ERP 9 installations efficiently and effectively because it enables you to:
Manage Licenses
Perform Central Configuration
Manage Users
Manage Company Profile
Manage Accounts
Change Passwords
Maintain Activity History
(d)Self-service using Knowledge Base
Tally has compiled a large selection of articles for users to understand the product and its applications. Users can access the Knowledge Base and search from available topics at their convenience.
(e)Software Assurance Services
Get instant product updates and upgrades as and when they happen
(f)Data Synchronisation Services
Now exchange data with ease between two or more Tally licenses (implemented at different locations)
requirements for remote connectivity – Access information via SMS,
Anywhere, Any Tally.ERP 9 Installation : You can access your Tally.ERP 9 companies from anywhere using even a Tally.ERP 9 in Educational Mode, and an internet connection. When your employees are at clients' locations, they can view the stock availability and commit delivery dates to the clients, or check the pending receivables from the clients. This will ensure availability of the latest details at that moment.
Security and Control : You have complete control on who can access your companies, and which features are available to the user. Further, your data will always be in your computer. Whenever a user connects to your company, based on the access permissions you have provided, the user can access the required features. If your employee is at a client's place and want to print an invoice or purchase order placed by the client, it can be done. However, the employee will not view your financial reports unless you have given the permission. If you want to check your financial reports when you are away from your office, you can use any computer with a Tally.ERP 9 installation and view the reports.
Record or Alter Vouchers : The user with the required permissions can create or alter vouchers. If you or your employee meets a supplier, and strike a favourable deal, a purchase order can be raised immediately from your Tally.ERP 9 company.
Audit Accounts : You can allow your auditor to do verification of your books using remote access. For this, you just need to allow remote access to your company for the auditor's Tally.NET ID. Like you or your employees logging in to the company, auditor also can log in and do the work.
Print Reports and Vouchers : Users can open a voucher or report, and print it at the remote location. When your employee is at a client's place to collect receivables, after collection a receipt can be recorded and a voucher can printed for the client.
Easy Setups : Connect your company, and allow users to access your company from anywhere. Note that only users with valid Tally.NET IDs are allowed to access your company remotely. Your account ID (e-mail ID used to activate your license) is a valid Tally.NET ID. You can create Tally.NET IDs for users who need to log in to Tally.ERP 9 remotely, allow access to these IDs. Similarly, you can allow your accountants or auditor who have their Tally.NET IDs to log in remotely.
Features which are widely used to secure the data in Tally:
· Create a strong password policy
Setting a strong password policy for the Tally data shall help secure and safeguard the financial information of the company from unauthorized changes. the Administrator can set a password policy for all the Tally users while creating and managing passwords for their company.
· Voucher type security
The administrator in Tally can provide the department and role-based permissions of masters, voucher type and reports to different users based on the business requirement. Assigning Voucher Type level security shall help to control and restrict access of individual Voucher Type and report from different users. In case you need more enhanced security to prevent your Tally data like more type of access, providing Backdate or cutoff date for each voucher types etc. you can check out Voucher Type Level Security Module.
· Secure data access
Confidentiality of the data is a major concern of every business owners today, thus every business must take steps towards preventing the visibility of data location from its users which is possible only by centrally managing all the data center activities i.e. through data server and hiding the actual location of data files. Centralized data server management helps to monitor and keep track of User activities or patterns on a daily basis which is possible only through Tally.Server 9 a Tally Solution product which acts as a data server who manages the data files and helps access and operate Tally only by providing the Data server name. The location of the data file is not required.
· Install virus/malware protection software
Antiviruses help safeguard the data from malware and viruses attacks which if not taken care of leads to paying of a huge amount for release of data.
· Take a regular backup of your data
One of the best methods which every business must use on a day to day basis is taking backup of data on daily basis. Backup acts as a recovery system during unwanted situations and helps towards smooth business continuity. If you are in hurdle of manually taking backup every day then you should use Smart backup++, the module which automatically takes backup of the Tally data and stores the copy in multiple locations on a scheduled time.
Tally.ERP 9 (now Tally Prime) module – Auto Backup. When it comes to business data, necessary measures must be taken to ensure that it is safe and secure at all times. Data loss and data theft is a common issue these days that is faced by all – start-ups, small businesses and big enterprises alike. Thus, with the Tally.ERP 9 Auto Backup module, you can take a complete backup of your company’s data and download it on your computer or store it on the Cloud.
- Tally.ERP 9 Auto Backup module is easy to install and use.
- There is no human intervention required as the backups are automated.
- It offers greater security and is very reliable.
- It helps safeguard the company’s data by ensuring it is backed-up daily or at regular intervals.
- It can be synchronized with free Cloud storage platforms like Google Drive, OneDrive, Dropbox, amongst others provided it has been installed on your local system.
By using the Auto Backup module, companies can save time and money as they can easily restore data at a click of a button. In the event of a system crash or a hack attempt, auto backups will ensure that the productivity at work is not hampered. Also, it helps build trust amongst your clients/customers, thereby improving your company’s credibility.
Tally.ERP 9 Auto Backup Features
- One-click installation and simple management.
- Manual deletion of unwanted backups.
- Date and time-wise backup to save Memory Space
- Schedule backup on a daily basis or at regular intervals.
- Fast Backup, irrespective of the network system (Lan or WiFi base)
- Option to take backups of selective companies or all companies.
- Automatically fetches the company’s data path from Tally.
- The flexibility of storing backups locally, on Cloud or an offsite location.
Automated Backup
This feature allows the user to safeguard his company data. The Automated Backup or Auto Backup is a capability that automatically takes data backup in the background without any disturbance or affecting your work.
Auto Backup can be carried out by executing the following steps:
Go to Company Creation/Alteration screen of the required company.
Set Yes to Enable Auto Backup as shown:
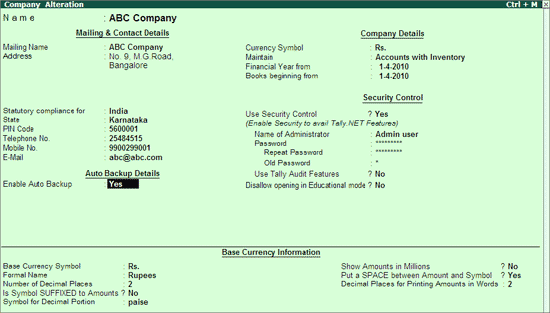
Save the Company Creation/Alteration screen.
The data backup is stored in the data folder of the respective company.
E.g.: A company titled ABC Company has a folder 10009 located in C:\Tally.ERP9\Data. On enabling Auto Backup feature the backup file ABK.900 is created in C:\Tally.EPR9\Data\10009
Restoring Auto Backup Data
To restore the auto backup taken execute the following steps:
From the Gateway of Tally
Press Ctrl + Alt + K.
Restore Company on Disk screen appears.
The Source field displays the data path of the company under Select Auto Backup to Restore screen. Press Enter.
The List of Auto Backup(s) will list all the companies enabled for Auto Backup.
Select the required company and press Enter.
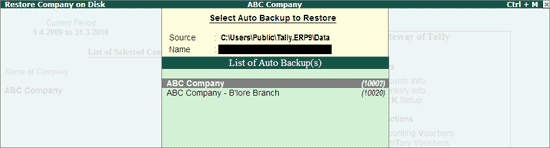
The List of Auto Backup Versions screen appears listing the backup versions.
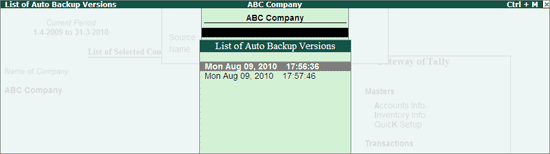
Note: List of Auto Backup Versions will contain backup version on daily basis.
The maximum days of backup versions listed will be of 60 days.
Select the required version from the list and press Enter.
The selected version of data backup is restored to the respective company folder.
The auto backup utility prompts the user to overwrite the existing company.
Press Y or click Yes to proceed with restoring the data.
Press Alt + F1 to Shut the existing company.
Select the restored company.
Accessibility
Companies that opt for a paperless audit can provide increased accessibility to financial documents and statements for auditing personnel. Increased accessibility can decrease the amount of time required by accounting and financial staff to provide documents to auditors.
tracking ability
Most paperless audit systems offer reporting and tracking abilities throughout the auditing process. Managers from the company being audited as well as the auditing firm's management can easily track and monitor each step in the review process. This increased tracking may help streamline resource requirements and helps manage the auditing timeline.
faster review
A paperless audit may take less time than a traditional audit process. Financial documents can be easily loaded for review and analysis with greater accuracy. Electronic processing of audit tasks minimizes human errors and the need to manually enter information into an auditing system. Electronic reviews may take less time than in-person physical meetings with paper forms.
increased security
Physical documents are more difficult to secure than electronic documents. Electronic data and documents can be secured through passwords and other digital security methods. Physical documents can be copied, lost, or placed in an unsecure location.
less waste
Reducing the need for duplicate copies of financial documents, storage facilities and office supplies can reduce the amount of waste both companies generate. Paperless audits use less paper, ink toner, electricity and office supplies than a traditional paper-bound audit. The reduction in paper and associated supplies can offer cost savings and an ecological benefit. This green focus may be important for companies that want to promote their company as being environmentally-friendly.
Limitations of E-Auditing
i)Requires Technology
Auditors must be comfortable using computer software to create audit reports. If an auditor is not familiar with computers or with the software he is expected to use, he may have a steep learning curve. Auditors also must be familiar with using email or websites and uploading attachments, while business owners must be able to retrieve audit reports from their email or by going to a website
ii)Security Considerations
If an auditor is going to use computers or other technology to prepare an audit, she must consider security factors that auditors who create paper reports don't have to consider. Audits often refer to sensitive information, such as a business' finances or tax requirements. Auditors must be able to send this information securely; only employees of the company who need to know the information in the report should be able to access audit reports online or via email.
iii)Different Filing Requirements
The Internal Revenue Service and other government agencies may have different rules for electronic record keeping than for paper record keeping. Business owners should find out how to store audit reports and for how long they must store them prior to agreeing to an electronic audit. In addition, although electronic audits are often called "paperless," some paperwork may need to be printed to fulfil government record-keeping rules.
Changing Over Systems
If a business relied on paper audits before, it has to switch over to an electronic system before it can begin taking advantage of paperless audits. This may take weeks or months, depending on how computer-based the business was before it switched over. In addition, some personnel may require training to access or use the new system. Thus, it can take a year or more for a business to switch over to a paperless system.
Auditing the auditors
In India the the National financing reporting agency have been set up as an independent regulator to regulate the auditors. NFRA is an independent review body over the audirtors and auditing firms with a view to improve the audit quality while retaining self-regulation mechanism by the professional body of auditors.
As per section 132(2) of the Indian Companies Act,2013, NFRA shall make recommendations to the government on formulation of accounting and auditing policies and standards.Most importantly NFRA will oversee the quality of service of the professions associated with ensuring compliance with accounting and auditing standards and suggest measures for improvement in quality of service.
NFRA has the twin powers of investigation and judicial powers of a civil court- It consists of government appointee chairperson,three full time and nine part time members with a term of three years each.
- the functions of NFRA include the standard setting, monitoring, review and overseeing the quality of service and enforcement.
Indian Accounting Standards-Unit 1 click here
Comments
Post a Comment